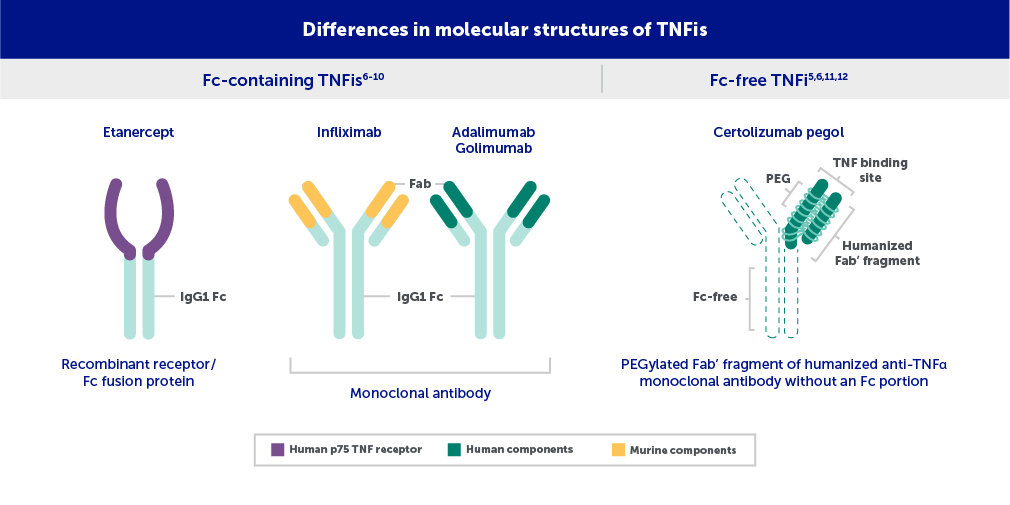
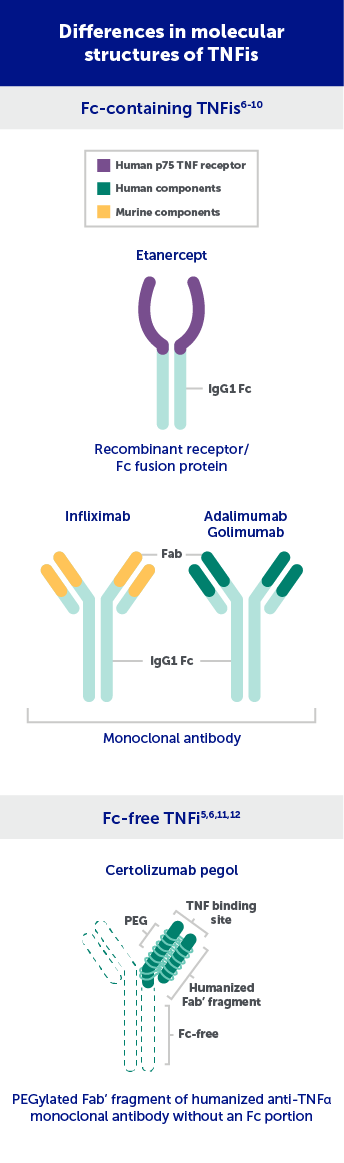
Differences in TNFis May Impact Treatment Outcomes in RA Patients with High RF
Many TNFis contain an Fc region, which can potentially be affected by high RF levels.6-10 Because RF binds to Fc fragments, higher RF levels may be associated with greater drug clearance of Fc-containing TNFis, resulting in lower active drug concentrations.5,6,11,12
These images are not meant to compare efficacy or safety. The clinical relevance is unknown.
Fab’=fragment antigen-binding; Fc=fragment crystallizable; IgG=immunoglobulin G; PEG=polyethylene glycol; TNF=tumor necrosis factor; TNFi=tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
Figure adapted from Porter C, et al. Certolizumab pegol does not bind the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn): Consequences for FcRn-mediated in vitro transcytosis and ex vivo human placental transfer. J Reprod Immunol. 2016;116:7-12, with permission from Elsevier.
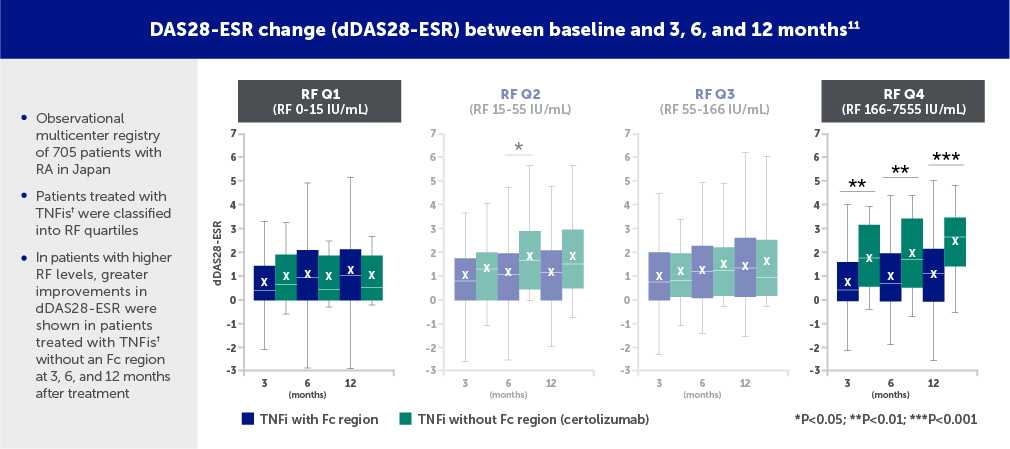
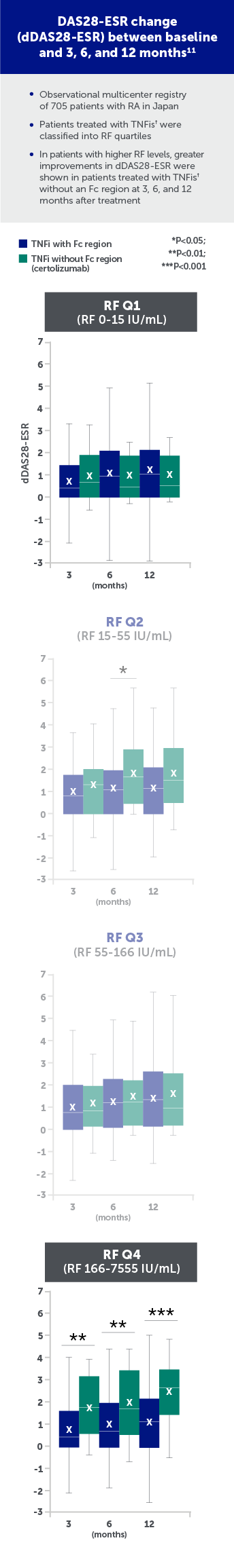
ANSWER Cohort Study
A retrospective study using data from a Japanese registry (the ANSWER cohort) revealed that there was differential efficacy of TNFis based on the presence/absence of the Fc region.† Treatment with the Fc-free TNFi resulted in significantly lower Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) scores in patients with high RF levels (>166 IU/mL) at 12 months vs patients treated with other Fc-containing TNFis.11
†TNFis with Fc: adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, golimumab; TNFi without Fc: certolizumab.
Certolizumab=certolizumab pegol; dDAS28-ESR=change in Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate; Fc=fragment crystallizable; IU=international units; Q=quartile; RA=rheumatoid arthritis; RF=rheumatoid factor; TNFi=tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
Figures adapted from Nakayama Y, et al. Differential efficacy of TNF inhibitors with or without the immunoglobulin fragment crystallizable (Fc) portion in rheumatoid arthritis: The ANSWER cohort study. Rheumatol Int. 2022; Jul;42(7):1227-1234. Used with permission from Sprinter Nature
EXXELERATE Trial
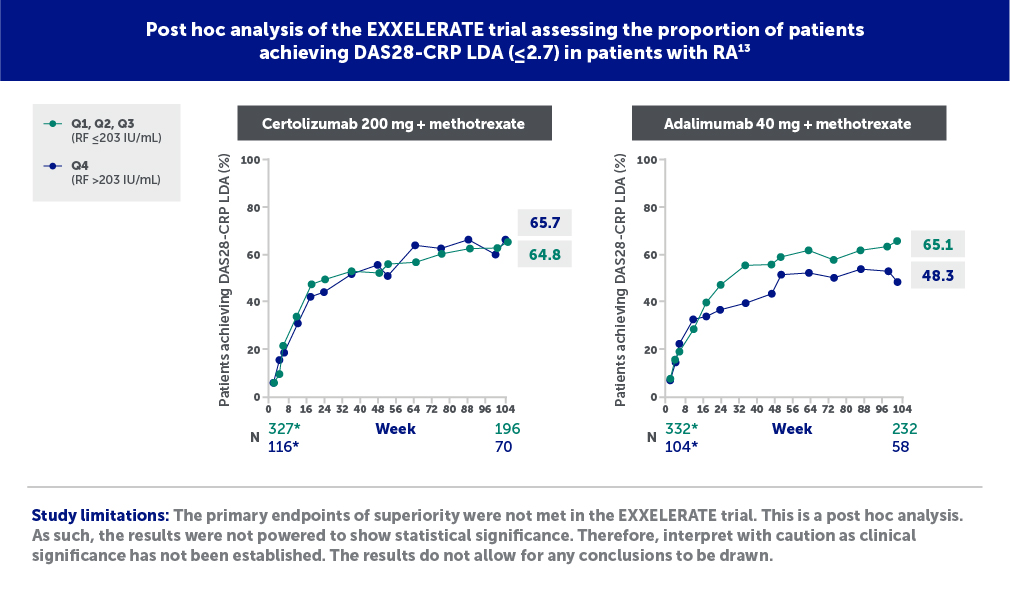
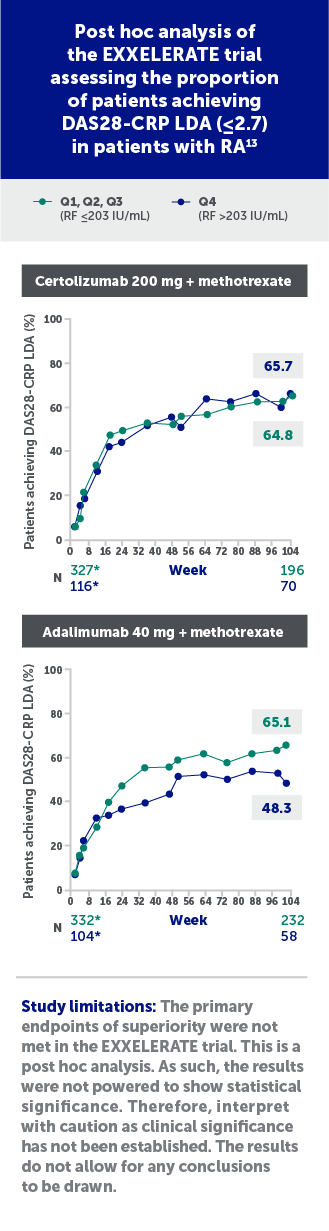
The recent post hoc analysis of the EXXELERATE study has also demonstrated that certolizumab-treated patients showed consistent efficacy across baseline RF quartiles in patients with RA.13
*Number at Week 2.
Certolizumab=certolizumab pegol; DAS28-CRP=Disease Activity Score 28 with C-reactive protein; IU=international units; LDA=low disease activity; N=number; Q=quartile; RA=rheumatoid arthritis; RF=rheumatoid factor.
Figures adapted from Smolen J, et al. Do high RF titers impact response to TNF inhibitors? Comparison of certolizumab pegol and adalimumab in patients with RA and high titers of RF: A post hoc analysis of a phase 4 trial. ACR Convergence 2023, poster 2148. Used with permission from American College of Rheumatology
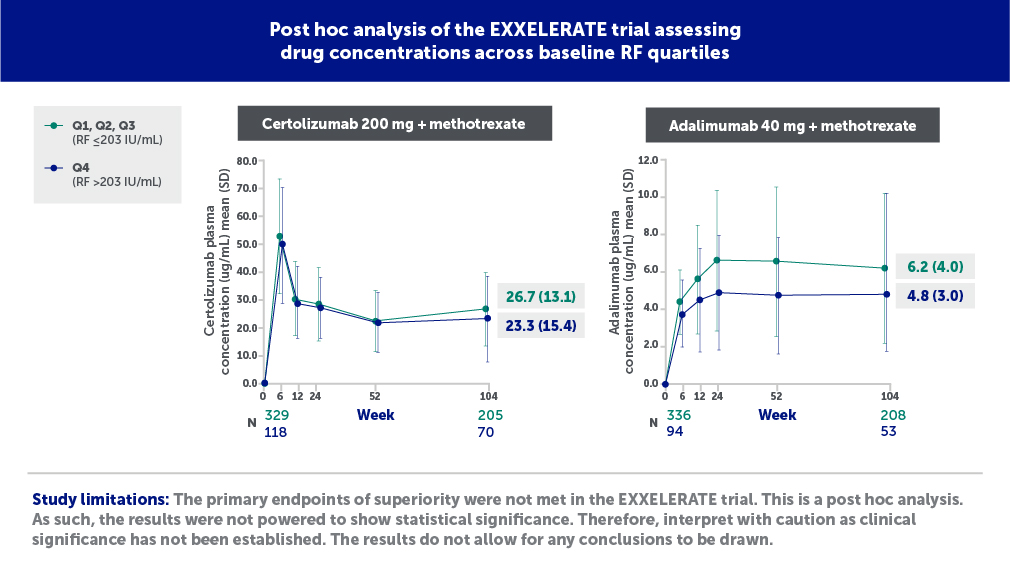
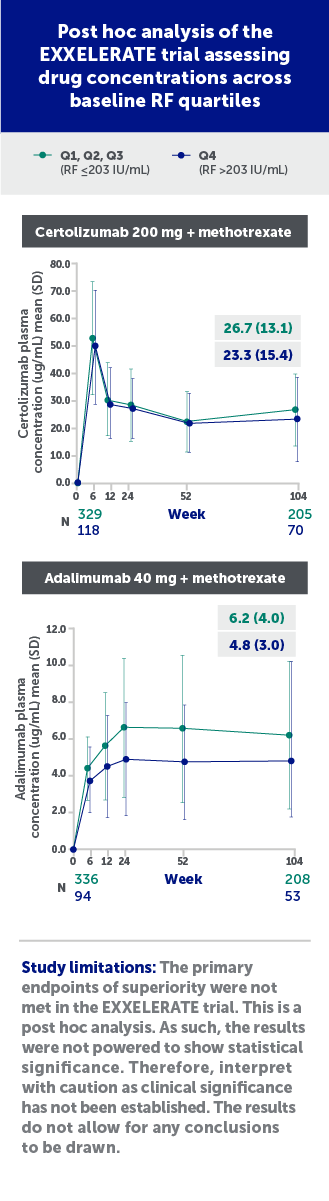
The post hoc analysis of the EXXELERATE trial showed that certolizumab-treated patients with RA had similar drug concentrations across baseline RF quartiles.13
Certolizumab=certolizumab pegol; IU=international units; N=number; Q=quartile; RF=rheumatoid factor; SD=standard deviation.
Figures adapted from Smolen J, et al. Do high RF titers impact response to TNF inhibitors? Comparison of certolizumab pegol and adalimumab in patients with RA and high titers of RF: A post hoc analysis of a phase 4 trial. ACR Convergence 2023, poster 2148. Used with permission from American College of Rheumatology
Considerations For Clinical Practice
Recent studies, including the EXXELERATE post hoc analysis, have shown that certolizumab-treated patients with RA and high RF had similar drug concentrations and clinical responses to patients with RA and low RF levels, a pattern not observed in patients treated with other Fc-containing TNFis.5,11,13
These data suggest that RF levels should be considered when making treatment decisions for patients with RA, and that certolizumab may be a suitable therapy for patients with RA and high RF.14
Watch Video: Clinical Relevance of High Rheumatoid Factor in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Watch Josef Smolen, professor of Internal Medicine and Chairman of the Division of Rheumatology at the Medical University of Vienna, discuss new data about RF and how it may be a biomarker that allows better understanding of which patients will respond better to a particular therapy.